Post Stroke OSA: the effect of intermittent hypoxia on cerebrovascular recovery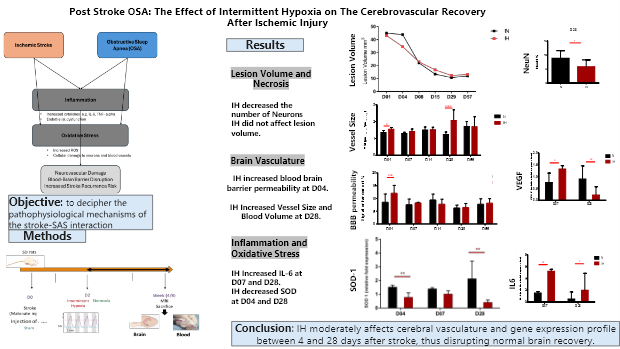
Laboratories : HP2 and GIN - 01/10/2021 – 30/09/2024Thesis project holders : Anne BRIANCON-MARJOLLET and Claire ROMEYoung thesis researcher : Bayan EL AMINE Abstract: Stroke affects 15 million people annually, often impairing cognitive function. Post-stroke recovery is prolonged, worsened by comorbidities like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which impacts 30% of patients. This thesis studied stroke-OSA interaction in rats where ischemic lesions were induced and exposed to hypoxic (IH) or normoxic (N) conditions... Read more |
Crosstalk between C1 and HMGB1 alarmin in inflammation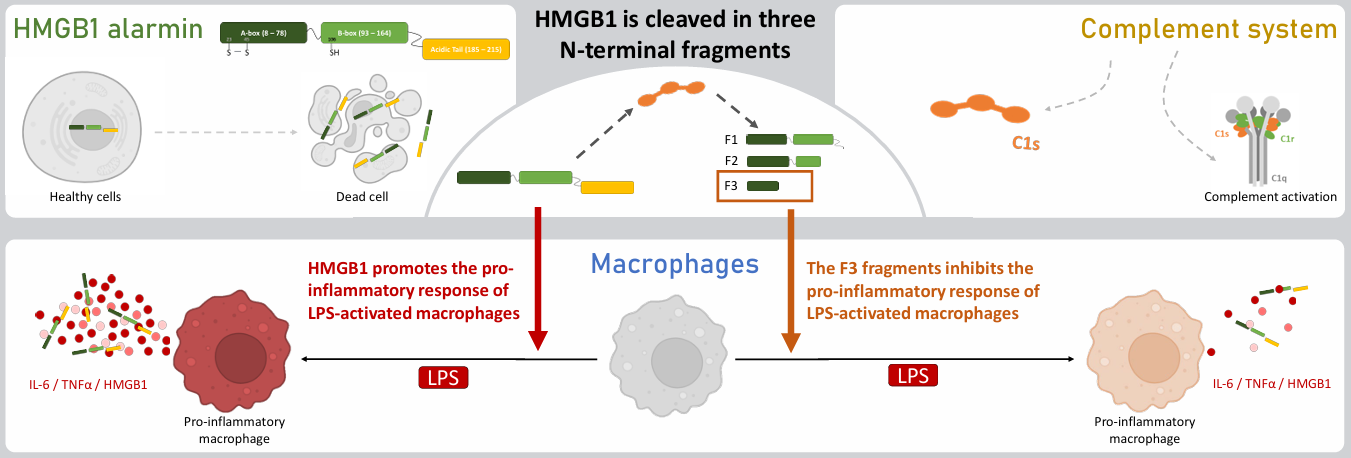
Laboratories : IBS and LCBM - 01/09/2021 – 30/09/2024Thesis project holders : Véronique ROSSI and Thierry RABILLOUDYoung thesis researcher : Marie LORVELLEC Abstract: C1s protease initiates the classical complement pathway, previously thought to target only C2 and C4. Recent studies reveal that free active C1s has roles beyond complement activation, including targeting HMGB1. Initially recognized as a nuclear protein, extracellular HMGB1 drives inflammation. This work highlights that fragment f3, generated by C1s cleavage, inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion... Read more |
Investigation of the redox signaling involved in the chloroplast biogenesis
PI : David COBESSI and Robert BLANVILLAINPHD : Soumiya SANKARI MUTHUKUMAR Abstract: The thesis investigated activity of the superoxide dismutases PAP4 and PAP9 from the PEP. The PEP envelope was calculated at 27,5 Å resolution, and the CSP41b 3D structure solved at 3.4 Å resolution. Its interaction with PRIN2 was investigated using biophysical experiments and tested in onion epidermal cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay. For fishing PRIN2 interactors, a proximity labelling strategy was designed. Genetic constructions were cloned and tested in transient experiments, proving its feasibility. These studies are part of a broader project that aims at highlighting functional innovations in angiosperms around PEP-specific plastid transcription. Read more |
Telomeric response to potentiate new theranostic approach in ratio-resistant lung cancer cells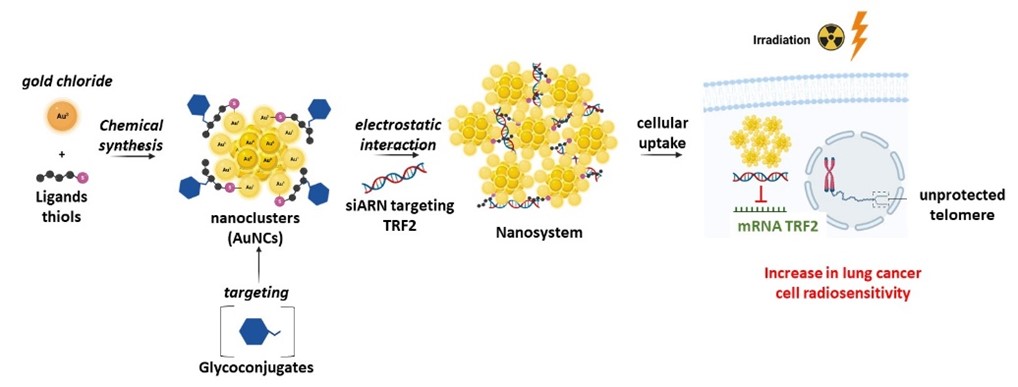
Laboratories : IAB and DCM - 01/10/2020 - 01/10/2023PI : Virgine FAURE et Olivier RENAUDETPHD : Sean MORO Abstract Our project was to overcome radioresistance in lung cancer cells by combining radiotherapy with a theranostic system using radiosensitizing gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) able to deliver siRNA targeting TRF2 protein, one of the key players in telomeric radioprotective response. Following the synthesis and characterization of the nanosystem, our results have shown that AuNCs were capable to interact with siRNA, to protect them and to deliver them efficiently into lung cancer cells. We demonstrated that this nanosystem increased significantly the radiosensitivity of lung cancer cells after X-rays exposure. Finally, the specific targeting of tumor cells was improved by modifying the surface of AuNCs in order to target GLUTs transporters, which are overexpressed in a wide variety of cancers. Read more |
Design of cell-permeable and fluorogenic delivery agents to extend the spectrum of antibiotic action
PI : Yung-SIng WONG and Eric FAUDRY PHD : Pascal MOSER Abstract: An important scientific need is to understand how a sufficient translocation of bioactive molecules across the Gram-negative cell wall can be assured. An original mean in this project was the use of cyclic peptides as carriers to improve antibiotics transport through the bacterial cell wall due to their remarkable mechanism of conformational changes (validated by computational modeling). Cyclic peptides, coupled with antibiotics, were synthesized in attempts to broaden the spectrum of antibiotics. We also designed a new promising self-immolative linker (SIL) aimed at delivering carboxylic antibiotics inside the bacteria. This was explored by the development of a selective redox-sensitive fluorogenic SILs to detect the release of carboxylic acids inside bacteria. Read more |
Optimization of electrochemical transduction using aptamers for the detection of arginine vasopressin in the picomolar range
PI : Michael HOLZINGER and Corinne RAVELET |
Impact of intermittent hypoxia on wound healing in experimental models of diabetic foot ulcers
PI : Matthieu ROUSTIT - Walid RACHIDI and Jean-Luc CRACOWSKI |
Fighting oxidative stress thanks to nisod mimics
PI : Pascale DELANGLE and Carole DUBOC PHD : Pawel GUINARD Abstract: The objective of this thesis was to create biomimetic complexes inspired by the nickel superoxide dismutases’ (Ni-SOD) active site to replicate its efficient antioxidant activity. These complexes are based on a pseudo-ATCUN scaffold (Amino-Terminal CuII and NiII binding motif), capable of reproducing the NiII geometry in the enzyme's active site. The obtained results have identified two reaction intermediates formed during the dismutation of superoxide by one of these complexes, providing valuable insights into the enzyme mechanism. Additionally, through the identification of factors enhancing SOD activity, highly efficient complexes have been developed, showing potential as antioxidant agents within cells. Read more |


